What is a gallium nitride power transistor?
- Share
- Issue Time
- Mar 1,2024
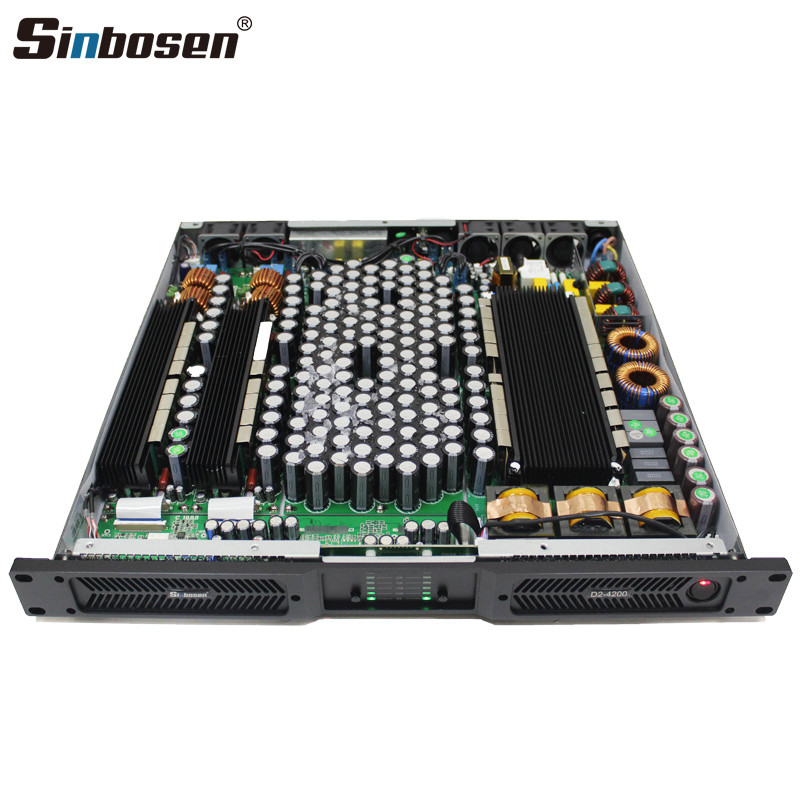
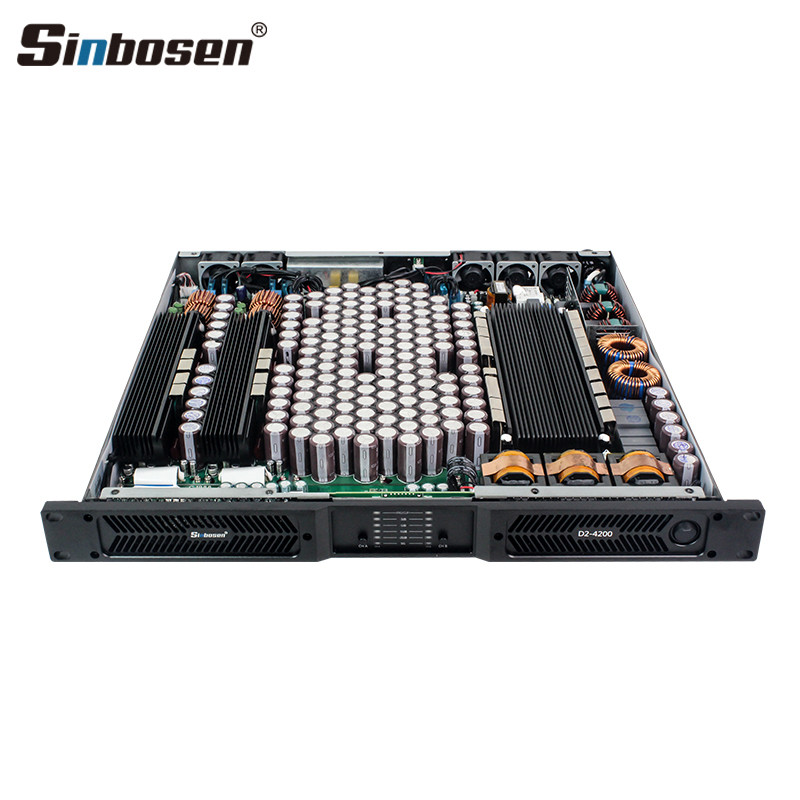
Gallium nitride power tube is a new type of electronic component that is very suitable for some audio applications that require high performance, high efficiency and high power output. Sinbosen has also applied this material to its D series digital power amplifiers, making the performance more stable, reducing noise, and bringing a better sound experience. At present, all the D series digital amplifiers shipped by Sinbosen domestically have been upgraded to gallium nitride materials. However, there are still a few digital amplifiers made of non-gallium nitride materials left in overseas warehouses. Please pay attention to the distinction when placing orders.
Silicon MOSFETs have historically been the switching transistor of choice for Class D systems. Although their amplifiers were more efficient, they were plagued by heavy distortion due to imperfect switching, high on-resistance, and very high stored charge. These charges dissipate power and cause ringing, resulting in greater distortion. | |||
|
Limitations of silicon MOSFETs in audio equipment: |
|||
|
High switching losses: When a MOSFET turns on or off, it experiences a brief period of high power consumption. These switching losses reduce efficiency and increase heat. In Class D audio systems, high switching losses reduce output power and overall system efficiency. Bandwidth Limited: The switching performance of silicon MOSFETs limits the switching frequency of the output power stage. This limitation reduces efficiency and output power. Thermal limitations: Silicon MOSFETs generate significant amounts of heat in high-power Class D audio systems. To overcome this limitation, many designers use large heat sinks, which increases the size, weight, and cost of the system. Gate drive constraints: The gate drive voltage must be fast and accurate to ensure efficient switching. In Class D audio systems, the limitation of gate drive is that the gate turns on slowly, thereby reducing efficiency and increasing distortion. |
|||

Why do audio devices use gallium nitride materials?
|
Advantages of audio amplifiers using gallium nitride devices:
|
|||
|
Faster switching speed: Gallium nitride devices have higher electron mobility than silicon devices and therefore switch faster than traditional silicon MOSFETs, reducing switching losses and improving overall efficiency. Higher switching frequencies allow more precise control of the output waveform, resulting in lower distortion, higher fidelity, higher bandwidth and faster transient response. Lower on-resistance: Because gallium nitride devices have a wider bandgap than silicon devices, GaN FETs have significantly lower on-resistance and conduction losses compared to traditional silicon MOSFETs, resulting in lower power consumption and achieve higher output power. This allows amplifiers to be more efficient, require less cooling and be smaller in size. Reduced component count: Designs using GaN devices with higher switching frequencies can use fewer, lower-cost external components compared to traditional silicon-based designs, simplifying amplifier design and reducing overall cost. Lower distortion: GaN FETs have lower parasitic capacitance and inductance, reducing distortion and improving overall fidelity. Smaller form factor: GaN devices are smaller than silicon devices at the same performance specifications, allowing for smaller, more compact amplifier designs. |
|||

