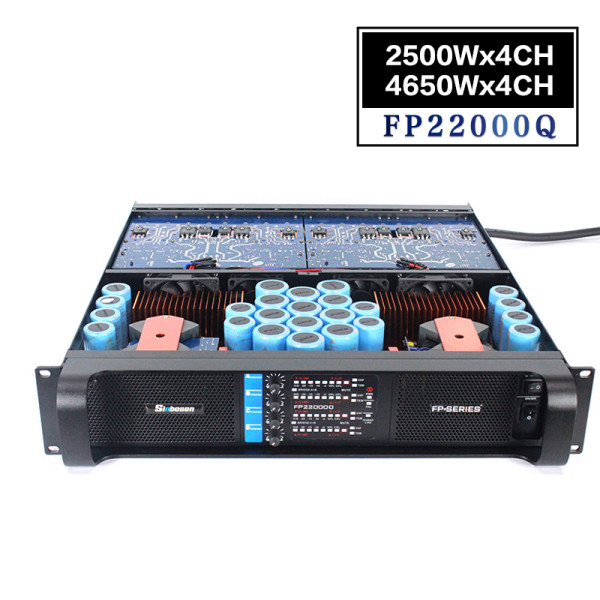
What is a heat sink?
- Share
- Issue Time
- Aug 31,2022
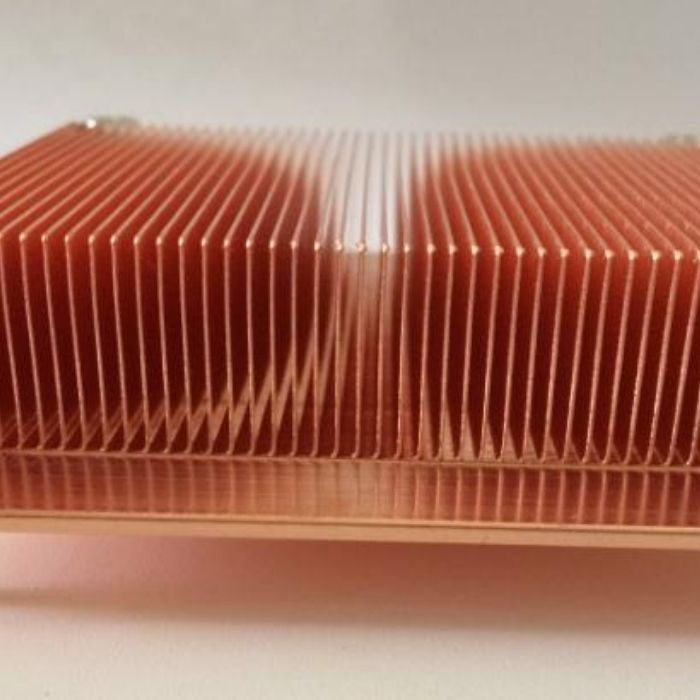
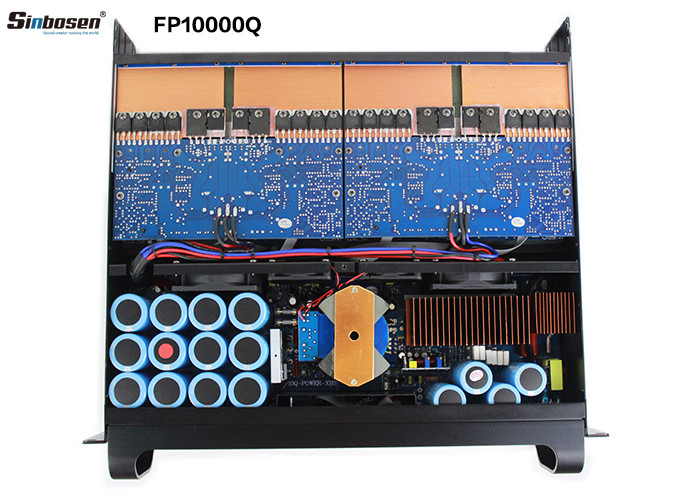
The heat sink is a device for dissipating heat for the heat-prone electronic components in the electrical appliance. Mostly made of aluminum alloy, brass or bronze into plate, flake, multi-flake, etc.For example, the CPU central processing unit in a computer needs to use a fairly large heat sink. The power tube, the line tube in the TV, and the power amplifier tube in the power amplifier should also use the heat sink.
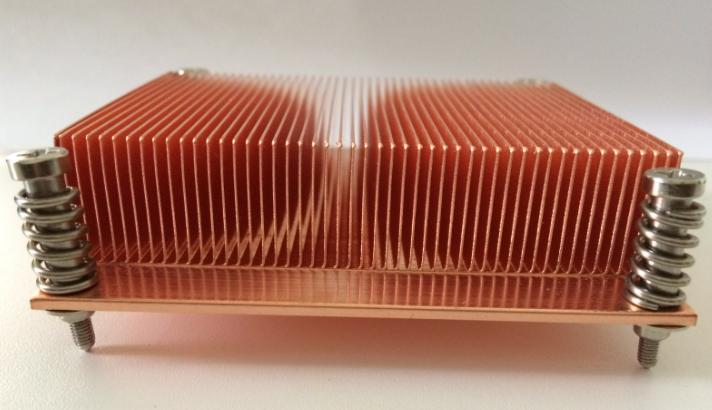
The principle of heat sink heat dissipation is to increase the surface area to speed up heat dissipation. The material used as the heat sink is a metal with a small specific heat, which absorbs heat very quickly and dissipates heat relatively quickly, so that the effect of rapid heat dissipation is achieved through heat transfer.
Generally, the heat sink should be coated with a layer of thermal grease on the contact surface between the electronic component and the heat sink during use, so that the heat emitted by the component can be more effectively conducted to the heat sink. It is then dissipated into the surrounding air through the heat sink.
As far as the heat sink material is concerned, the thermal conductivity of each material is different, and the thermal conductivity is arranged from high to low, namely silver, copper, aluminum, and steel. However, it would be too expensive to use silver as a heat sink. Copper and aluminum are the best and most cost-effective solutions. Sinbosen's amplifiers are made of these two materials.
The radiator is a device that accelerates the heat dissipation of the heating body. There are two points to measure the quality of a radiator: heat dissipation and quietness.
For example, a large number of integrated circuits are used in computer components, as are ic power amplifiers. As we all know, high temperature is the enemy of integrated circuits. High temperature will not only cause the system to run erratically, shorten the service life, and may even cause some components to burn out. The heat that causes the high temperature does not come from outside the amplifier, but inside the integrated circuit. The function of the radiator is to absorb the heat, and then dissipate it to the inside or outside of the case to ensure that the temperature of the computer components is normal. Most radiators absorb heat by contacting the surface of the heating component, and then transmit the heat to a distance through various methods. For example, in the air in the chassis, and then the chassis will transfer the hot air to the outside of the chassis to complete the heat dissipation of the computer.




