The difference between built-in crossover and external crossover?
- Share
- Issue Time
- Jul 27,2022
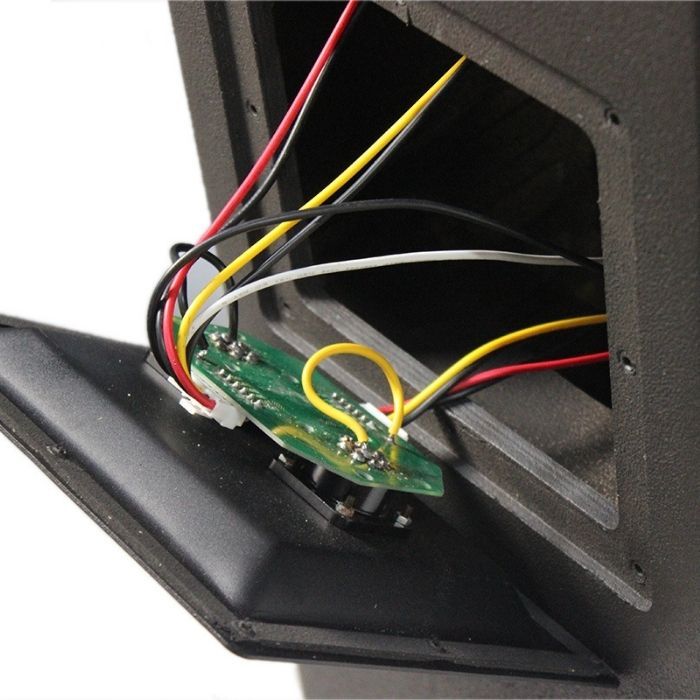

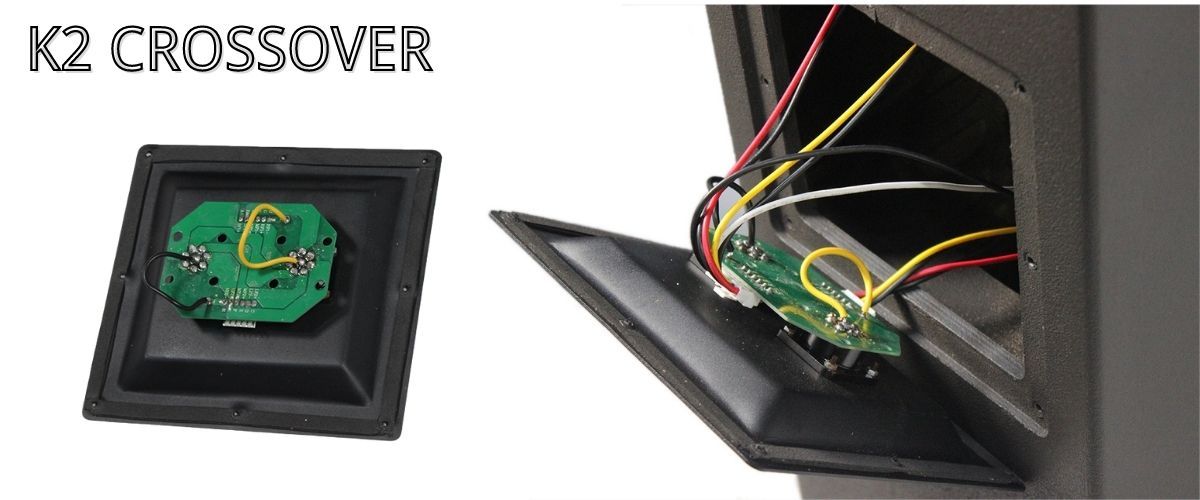
What is a built-in crossover?
In fact, there is a crossover board inside the speaker. When the amplified audio signal is transmitted, it will transmit the high frequency and low frequency of the signal to the treble driver and bass driver of the speaker according to the frequency division point designed by the driver of the speaker. This is also a common power crossover, also called passive crossover.
In the audio system, although the built-in crossover is the most common, it does not fully meet the needs of all our systems. When speakers don't have power crossover boards to keep the audio frequency band going, system engineers need to figure out a way to artificially divide them. The principle is to add a device with a frequency divider function before the power amplifier to divide the high frequency and low frequency signals in advance for the full-frequency signal in the weak current. After that, the signal current is amplified by the tweeter power amplifier and the bass power amplifier respectively, and is directly sent to the corresponding driver of the speaker. This frequency division method is called electronic frequency division, also called active frequency division.
Common external frequency divider circuit
We often have a question: Is the built-in crossover better or the external crossover better?
From an objective point of view, there is no such thing as absolute good or bad. For example, for the built-in 3-way speaker, we only need to give 1 full-frequency signal to the speaker power amplifier, and the audio signal amplified by the power amplifier is sent to the speaker. Then the frequency division board inside the speaker will divide the signal to the tweeter, midrange speaker and woofer according to the set frequency division point. In this way, we only need one power amplifier to complete it. First of all, it saves a certain cost, and in terms of debugging, the original understanding and presentation of the speaker by the speaker developer and designer is used, which shows the best sound quality effect of the factory default.
Works in the built-in three-way state
With the rapid development of the audio industry, there are more and more choices of speakers. Now many speakers on the market usually have two working modes: one is the built-in crossover mode FULL, and the other is the external crossover mode Bi-AMP, select the working mode of the speaker by adjusting the key.
As for the advantages and disadvantages of the internal and external frequency division, the previous article has been explained. On this basis, we did an experiment: using a processor to process the two working modes of a two-way speaker, let it play the same song in the external crossover mode and the built-in crossover mode respectively. As a result, the effect of the external crossover to release music is not as good as the built-in crossover, because when we use the external electronic crossover of the speaker, we only set the crossover to play directly, and the high and low frequencies are not fully connected. After some careful elaboration, the sound became somewhat intriguing.
What is the reason?
When using an external electronic crossover, the engineer needs to correct and adjust the data parameters in the sound reinforcement just like the speaker development and calibration work. This is like the sound quality of the tuner and the speaker is in PK. In the absence of a professional sound engineer, we prefer to choose the crossover mode effect set by the speaker factory, that is, the built-in crossover mode, which can help us restore the original intention of the speaker designer. Of course, you are a senior audiophile, and you have a good understanding of acoustics, phase, and electronic circuits. I believe that the external crossover can bring you even greater surprises!
1. Place different
①Built-in frequency divider: The frequency divider is installed inside the audio.
②External frequency divider: also known as active frequency divider, the frequency divider is installed outside the audio, and the external frequency divider has an electronic frequency divider or a processor to process the signal.
2. The characteristics are different
①Built-in frequency division: When the amplified audio signal is transmitted, the internal frequency division board is responsible for passing its capacitance, inductance, etc.
②External frequency division: For 3-ways audio signals of high, medium and low, there must be three power amplifiers to receive the 3-way frequency-divided signals respectively, and then transmit them to the corresponding drivers of the speakers after amplification.
3. Different advantages
①Built-in crossover: It does not fully meet the needs of all our systems. When speakers do not have a power crossover board to make the audio segment go its own way, the system engineer needs to find a way to artificially divide the frequency.
②External frequency division: The signals of each frequency band can be better utilized, and the selection of frequency bands is more flexible. The high, middle and low frequency frequency bands are more clearly focused on expressing their own frequency domain content.



